Abstract
Introduction
Cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) affects up to 20% of patients with cancer, and causes substantial morbidity and mortality. Although tissue factor has been most studied, several other mechanisms contribute to the development of CAT. Recently, a role for the contact activation pathway in pathologic thrombosis and in CAT has been recognized. We have observed that the cleaved form of high molecular weight kininogen (cHK), an a priori demonstration of contact activation, circulates in plasma in many patients with active cancer. Contact activation is initiated by the activation of factor XII (FXII) to FXIIa, and our studies as well as those of others suggest that circulating extracellular vesicles (EV) in cancer patients may mediate FXII activation. Polyphosphate (PP) is a known FXII activator, although other biological material such as RNA and DNA may also stimulate contact activation. Therefore, to better define the mechanisms of cancer EV-mediated FXII activation, we characterized the ability of exosomes, defined as EV of < 150 nm in size, to stimulate FXII activation in normal human plasma.
Methods
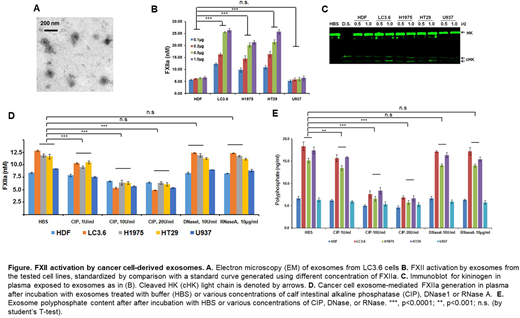
Exosomes were isolated using a multistep ultrafiltration method from HDF (human dermal fibroblast), LC3.6 (pancreatic cancer), HT29 (colorectal cancer), H1975 (non-small cell lung cancer), and U937 (monocytic lymphoma) cell lines. The quality of the exosome preparation was assessed using electron microscopy (Fig. A). Exosomes were quantified by measuring protein concentration (DC™ Protein Assay Kit II, Bio-Rad 5000112), and equal amounts of exosome, as judged by protein content, were added to citrated normal human plasma. FXIIa generation in plasma was quantified colorimetrically using the substrate H-D-prolyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-arginine-p-nitroaniline dihydrochloride (S-2302). Dextran sulfate was used as a positive control to induce FXII activation. Briefly, different amounts of exosomes, as determined by protein content (100 ng to 1 microgram), were added normal human plasma containing S-2302, after which the A405 was recorded. A standard curve was prepared by adding known amounts of FXIIa to the same plasma in parallel. Formed FXIIa activity induced by the exosomes was characterized by the relative purified FXIIa activity in the standard curve. Additionally, the generation of cHK also was assessed in exosome-activated plasma.
Result
Exosomes derived from cancer cell lines activated FXII in a manner concordant with the relative prothrombotic risk of these tumors, i.e. LC3.6 > HT-29 > H1975 > U937 = HDF (Fig. B). Coincident with the activation of FXII to FXIIa, exosomes induced the cleavage of high molecular weight kininogen to cHK in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. C). Since the mechanisms by which exosomes induce FXII activation have not been characterized, we assessed the roles of polyphosphate (PP), RNA and DNA expressed on the exosome surface. Pretreatment of exosomes from cancer cells with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), but not RNase or DNase, inhibited the ability of these exosomes to initiate FXII activation in a dose-dependent manner (Fig D). The maximal effect occurred at a concentration of CIP of 20 U/ml, and the relative reduction in FXII activating activity by exosomes from a specific cellular source was proportional to the maximal activity of the exosome preparation before treatment. A decrease in exosome PP content lead to a parallel reduction in FXII activating ability. (Fig.E).
Conclusion
These studies demonstrate that exosomes derived from both primary, non-transformed cells (HDF), as well as cancer cell lines have the ability to support FXII autoactivation in human plasma. Their ability to do is proportional to the relative risk of thrombosis associated with cancers derived from their parental cell lines. Treatment of exosomes with CIP substantially reduces the FXII activating capacity of those derived from the tested cancer cell lines and HDF. Human plasma exosomal PP is a constitutive potential source for contact activation that may be increased in cancer patients. Its relative contribution to thrombin generation via FXII activation versus that of tissue factor remains to be determined in individuals and in cancer types. However, neutralization of exosomal PP provides an additional pathway for prevention of cancer-associated thrombosis.
Schmaier:Biomotiv: Consultancy; Alnylam: Research Funding; Enzyme Research Laboratories: Honoraria; Shire: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Temple University: Patents & Royalties; Cleveland Clinic Foundation: Research Funding. Khorana:Pfizer: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal